Data sheet of Ceramic ball
Ceramic balls are rolling, spherical elements that are used in check and ball valves, bearings, and other mechanical devices that provide rotary or linear motion. Like other ceramic products, they are made from inorganic, nonmetallic materials that are processed or used at high temperatures. Outer diameter (OD) or width is an important physical specification to consider. Many ceramic balls feature a highly controlled geometry and an extremely smooth surface finish. Precision grinding removes cuts, scratches, scuffs, and other breaks in surface continuity. Processes such as hot isostatic pressing (HIP) are used to create products with a pore-free microstructure and micron-sized grains. Many ceramic balls exhibit much greater hardness than steel balls, resulting in longer life and improved reliability. Ceramic balls can also provide higher stiffness, lower thermal expansion, lighter weight, increased corrosion resistance, and higher electrical resistance than comparable steel products.
Ceramic balls are made from many different types of materials. Alumina, a compound that consists of aluminum and oxygen, is used widely because of its versatility and low cost. Typically, alumina is used in the alpha alumina structural form or combined with other materials to form alumina-silicon carbide, alumina-zirconia, aluminum nitride, and aluminum silicates such as sillimanite and fibrolite. Boron carbide has a higher hardness than alumina or silicon carbide (SiC), a dense compound with a relatively high thermal shock resistance compared to other ceramics. Cubic boron nitride (CBN) is second only to diamond in terms of hardness. By contrast, hexagonal boron is structurally weak and best suited for use as a high temperature lubricant. Other materials in ceramic balls include compounds that contain aluminum, carbon, calcium, magnesium, titanium, tungsten, and zirconia. Examples include calcium aluminate, cordierite, dolomite, graphite, kaolin, magnesia, metal boride, mullite, porcelain, sapphire, silicon nitride, spinel, steatite, titanium carbide, tungsten carbide, and zircon.
 Inert alumina ceramic ball Inert alumina ceramic ball
Inert alumina ceramic ball is widely used in many fields, such as petroleum, chemical engineering, fertilizer, environmental industry, etc. Being the covering and supporting material and tower packing for catalyst in the reactor, the ceramic ball has features of high intensity, high chemical stability and thermal stability, it withstands high temperature and pressure during the process, and also resists the corrosion from the acid, alkali and other organic solvent. The leading effects of ceramic ball are to increase the distributing spots of gas or liquid, also support and protect the activated catalyst from the rushing of the gas and liquid inside of the reactor.
Physical Properties
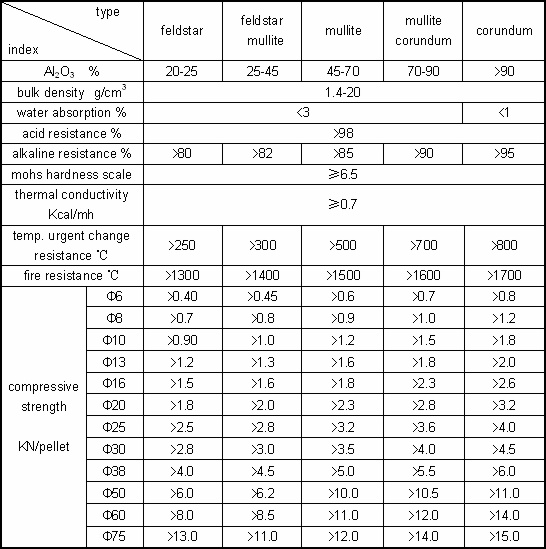
Chemical Composition??

Variety of Inert Alumina Ceramic Ball
In terms of Al2O3 contents, Inert alumina ceramic ball can be divided into 17 varieties, from 25% and with a gap of 5%.

- ?Remarks:
1. Al2O3 and SiO2 contents =92%
2. Al2O3 and SiO2 two ingredients contents may request by the customer.
3. bulk density data is for the reference only, not as the acceptance standard.
- Tolerance

 Perforated ceramic ball Perforated ceramic ball
Perforated ceramic ball is developed on the basis of inert ceramic ball. It has an adequate mechanical strength, good chemical and thermal stability as the normal inert ceramic ball, further more, it has larger surface area and free void which directly make the dispersion and flux of the fluids increased, and bring down the resistance of the system resulting from the perforated holes on the ball. As a new efficient catalyst support and covering material, it has been widely used in oil refineries, chemical, fertilizer, natural gas and environmental protection.
Main Performance

Tolerance

 Ceramic Alumina grinding ball Ceramic Alumina grinding ball
| The ceramic balls are broadly utilized as the covering or supporting materials of the catalyst in the reactors and the packing in the columns in such varied areas, for example, petroleum, chemical industry, chemical fertilizer, natural gas and environmental protection etc. Upon request, we select the optimum packing for the particular problem or application as well as the optimum material and size.
|
?Ceramic Ball Property
According to the alumina content different, we have five kinds of balls, the detailed specification as the table. |
Specification |
Common Ceramic Ball |
Inert Alumina Ceramic Ball |
Medium-Alumina Ceramic Ball |
Al2O3+SiO2 (%) |
>93 |
>92 |
>93 |
Al2O3 (%) |
17-23 |
23-30 |
47-56 |
Fe2O3 (%) |
<1 |
<1 |
<1 |
CaO (%) |
<0.5 |
<1.5 |
<2 |
MgO (%) |
<0.5 |
<2.5 |
<0.5 |
K2O+Na2O (%) |
<4 |
<4 |
<3.5 |
TiO2 |
--------- |
<0.5 |
<0.1 |
Leachable Fe2O3 |
--------- |
<0.1 |
<0.001 |
Water Absorption |
<0.5% |
<0.5% |
<2 |
Bulk Density?? g/cm3 |
2.3-2.4 |
2.3-2.4 |
2.6 |
Operation Temp (max)℃ |
>1100 |
>1100 |
1480 |
Moh s Hardness |
>6.5 |
>7 |
>7 |
Crush Strength |
KN/particle
|
1/8" (3mm) |
>0.35 |
>0.39 |
>0.45 |
1/4" (6mm) |
>0.5 |
>0.54 |
>0.56 |
3/8" (9mm) |
>0.94 |
>1.04 |
>1.16 |
1/2" (13mm) |
>1.5? |
>1.67? |
>1.56 |
3/4" (19mm) |
?>4.15? |
>4.21 |
>2.89? |
1" (25mm) |
>6.07 |
>6.22 |
>4.89 |
1 1/2" (38mm) |
>8.52 |
>8.92 |
>5.33 |
| 2" (50 mm) |
>9.7 |
>9.8 |
>6.22 |
|
|
 Heat storage ceramic ball Heat storage ceramic ball
Heat storage ceramic ball is characterized by its high strength, low abrasion loss, large heat capacity and thermal conductivity, excellent resistance to high temperature and the thermal shock. The product is widely used in recuperator in air separation process, and also used in blast furnace gas heating furnaces in iron & steel plants.
Main Performance

 Refractory ceramic ball Refractory ceramic ball
Refractory ceramic balls are mainly made of industrial alumina and refractory kaolin, processed by mixing, shaping and firing. Its high in mechanical strength and long life cycle, excellent chemical stability, and never reacts with the feeding material, excellent resistance to high temperature up to 1900 ?. It is widely used as support and covering packings for catalyst in shift converters, reformers, hydro converters, desulfurizers, and methanators, and can also be used as packings in hot blast furnaces and heater transformers in iron & steel industries.
|

